Deaing with Fibroids
Dealing With Fibroids |
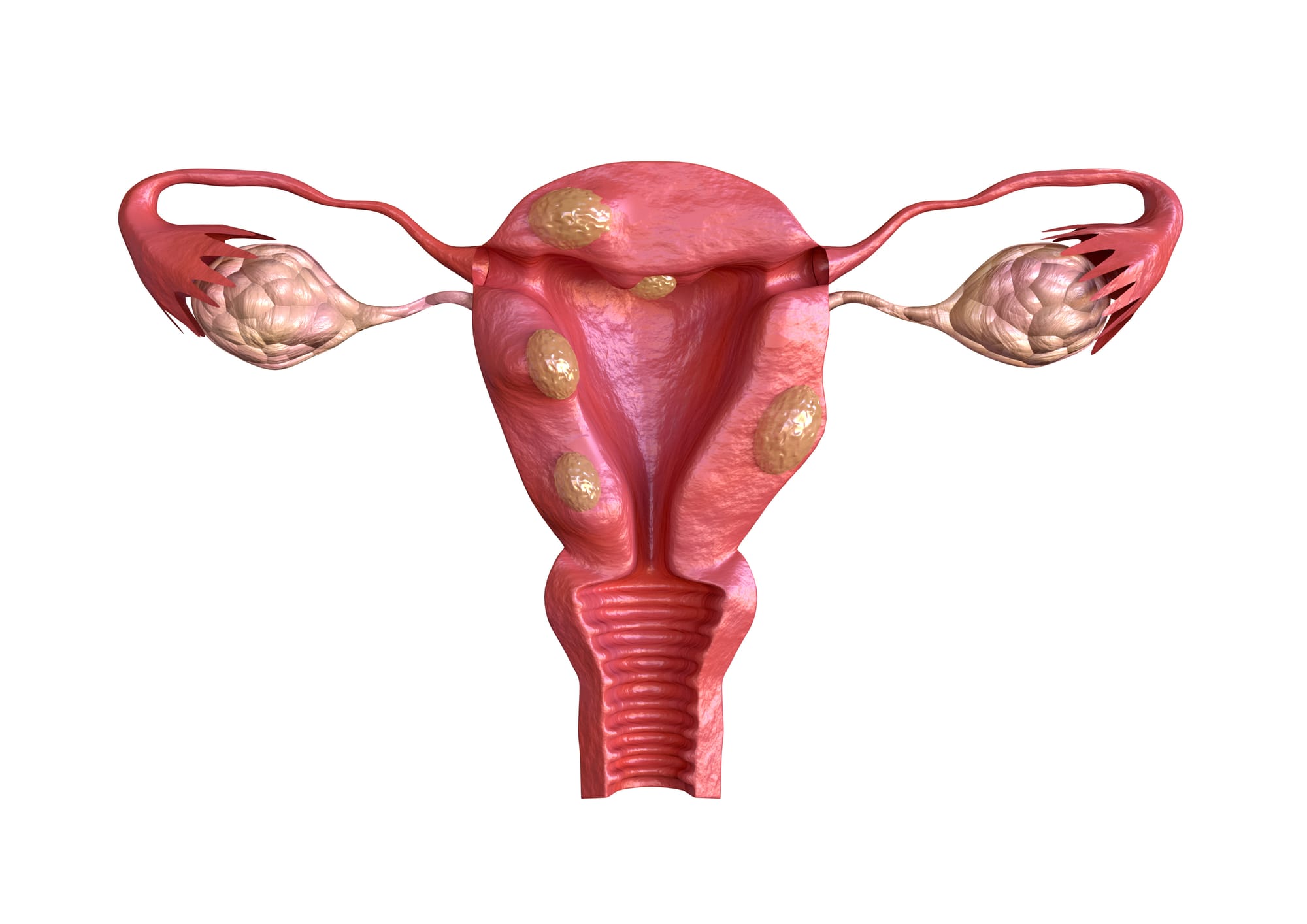
Fibroids are benign, non-cancerous overgrowths arising within the muscle layer of the uterus. Fibroids oftentimes do not cause any troublesome symptoms and, in such instances, do not require treatment. Many women, however, experience abdominal swelling, heavy menstrual bleeding, uterine cramping, pelvic or back pain, discomfort with intercourse, pregnancy loss, or urinary symptoms. Women with symptoms such as these may benefit from therapy to improve their quality of life.
There are many treatment options available for symptomatic fibroids. The therapy that your physician may recommend depends on the symptoms that you are experiencing, the size and location of the fibroids, as well as your future reproductive goals.
Options include –
- Expectant Management its a fancy term for do nothing That's right do nothing. This approach does not relieve symptoms and is best for women with minimal to no symptoms. Fibroids can with time become bigger or cause more problems. It may also be an approach for women nearing menopause when fibroid tend to become less problematic.
- Medical therapy- Several medications have come and passed but those that have shown some promise to slightly reduce symptoms and volume of fibroids are:
- Luprolide Acetate (Depo Lupron GnRH Agonist) FDA approved
- Elagolix vs Relagoliix (GnRH antagonist) FDA approved
- Ullipristal Acetate-not approved
- Radio Frequency Ablation (Acessa Procedure) is the surgical ablation of the fibroid that lie within the uterus. It is performed via laparoscopy through 2 small incisions or keyhole incisions. The aim of the surgery is to use radiofrequency ablation energy using an ingenious delivery system to destroys the fibroid where it lies within the uterus with cutting into or weakens it. This option allows for less pain, quicker recovery and less instability to the uterine wall if contemplating future childbearing.

- Uterine myomectomy is the surgical removal of the fibroids from the uterus. Myomectomy can be performed through a traditional abdominal incision or through a minimally invasive laparoscopic or hysteroscopic procedure. The aim of uterine myomectomy is to improve the symptoms a woman is experiencing, without physically removing the entire uterus. Indeed, a unique advantage of uterine myomectomy is that a woman’s reproductive options are preserved.

- Uterine fibroid embolization is a procedure in which an Interventional Radiologist inserts a small tube into the blood vessels that supply the uterus and inject small particles that impede blood flow to the uterus.
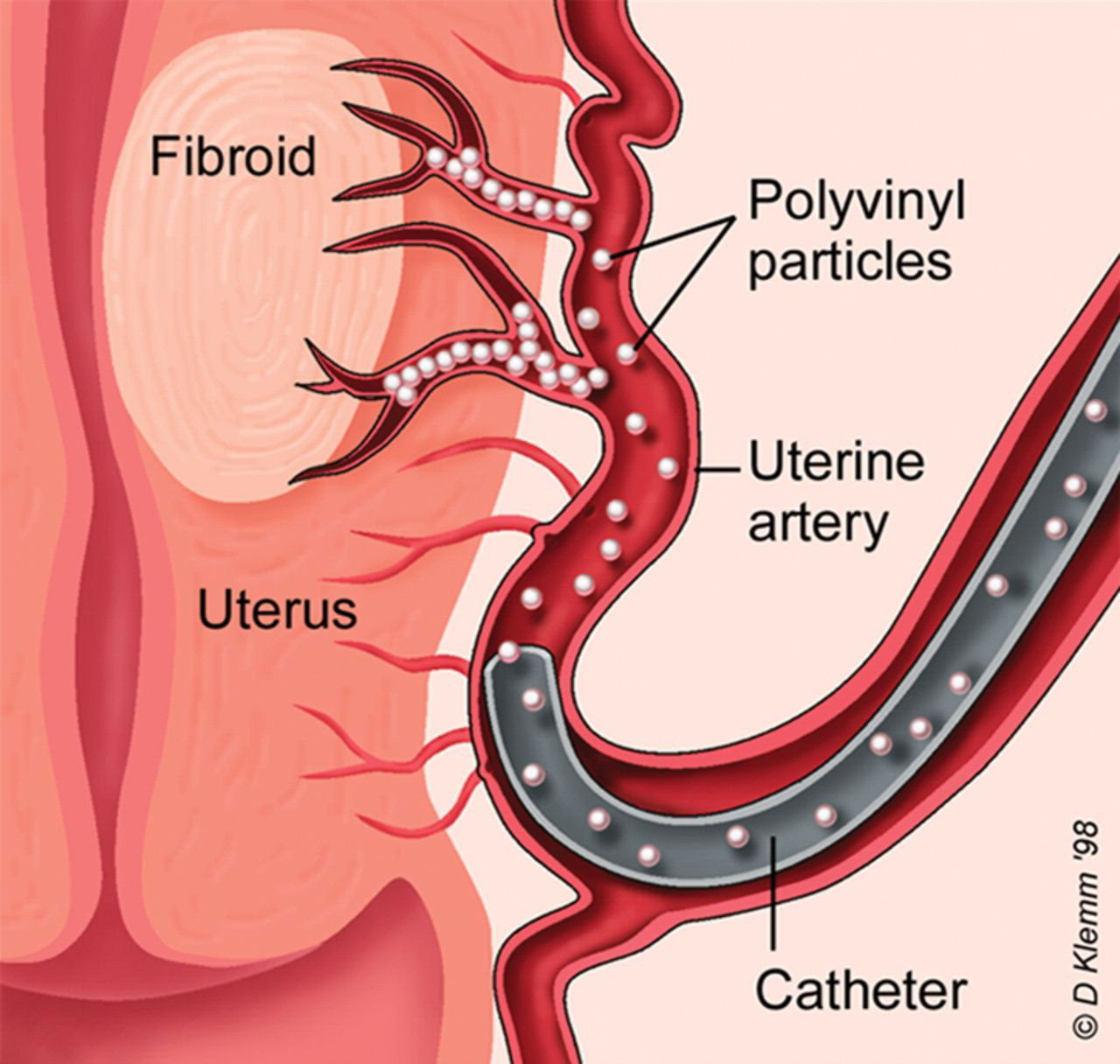 Disruption of the blood flow to the uterus will lead to shrinking of the fibroids and improvement in symptoms. Typically, this procedure is performed under light sedation and does not require general anesthesia.
Disruption of the blood flow to the uterus will lead to shrinking of the fibroids and improvement in symptoms. Typically, this procedure is performed under light sedation and does not require general anesthesia. - Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and all of its accompanying fibroids. Hysterectomy, historically performed through a traditional abdominal incision, can be performed via a minimally invasive vaginal or laparoscopic approach. Following hysterectomy, a woman would not expect to have menstrual bleeding. A common misconception is that a hysterectomy requires the removal of ovaries, which are responsible for a woman’s hormone production. In many cases, removal of ovaries is not required. Preservation of ovaries will provide a woman with her natural hormones until she enters the menopausal transition.
Fibroids can significantly affect a woman’s quality of life. As there are multiple, minimally invasive options for management of symptomatic uterine fibroids, women should consult with a minimally invasive gynecologic surgery specialist to discuss the treatment that is best for her.